


Biotin is a B vitamin (vitamin B7), also called vitamin H or coenzyme R. Biotin is found in a wide variety of foods, so biotin deficiency is rare. However, about half of all pregnant women can become mildly deficient in biotin. This deficiency may cause birth defects. Biotin in supplement form is used to treat brittle nails, hepatitis, neuropathy, and some other conditions. It is necessary for healthy hair growth. But can you take too much biotin?
As a water-soluble vitamin, biotin flushes easily from the body through the urine. Biotin is considered non-toxic and has no known side effects or maximum dosage. Even so, you should not take too much of it. Ask your doctor about taking more than the recommended amount.
If you think you aren’t getting enough biotin from the foods you eat, ask your doctor if you should take it in supplement form. Just remember that everyone is different and therefore can react differently. So if you suspect that you may be sensitive to biotin, cut back on the amount you are taking and consult your doctor. The following are possible side effects of biotin overdose.
1. Acne
Vitamin B7, biotin, increases the production of sebum in the skin, which contributes to dirt accumulation and ruptures. When too much biotin is taken, it can lead to cystic acne on the jaw line and the chin. It has been observed that when the biotin supplement is discontinued, the acne disappears within a few weeks. Take less 2,500 mcg of biotin per day, along with plenty of water, to avoid acne outbreaks.
2. Allergic Reactions
Fairly rarely biotin has caused allergic reactions in some people. Reactions may include swelling of face and throat, chest pain, tightness in the chest, nausea, and an itchy rash. If you experience any of these symptoms while taking a biotin supplement, stop taking the supplement immediately and see your doctor right away.
3. Pregnancy Effects
Can you take too much biotin? No. Pregnant and nursing women should not take a biotin supplement. Taking biotin supplements while pregnant can cause serious birth defects or miscarriage. There has been no conclusive scientific research to confirm this, but there does appear to be a definite connection. Always consult your doctor before taking biotin while pregnant.
4. Urination Frequency
Some people report the increase in the frequency of urination when taking high dosages of biotin. An increase in sweating has also been linked to high dosages of biotin. If you experience these symptoms, cut back on the amount of biotin you are taking and see if the problem works itself out. If not, see your doctor.
5. Diarrhea
Diarrhea and stomach cramps may flare up in some people when taking large amounts of biotin. If this happens to you, stop taking the supplements right away. Anytime you experience diarrhea, always drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
6. Nausea
When beginning to take biotin supplements, you may experience some mild nausea. This side effect will likely go away after a time. Take the biotin supplement with meals to see if that reduces the nausea. If not, reduce the dosage to see if that helps.
7. Increased Blood Glucose Levels
Can you take too much biotin? No. If you have diabetes, you probably should not take biotin supplements. Studies have shown that when vitamin B7 supplements are taken, fatty acids and glucose production are increased in the body. If you eat a wide variety of biotin-rich foods, you will get enough biotin without having to take the supplement. Talk to your doctor if you think you need extra biotin.
8. Drug Interactions
Ask your doctor if taking a biotin supplement will interact with any medication(s) you may be on, or before you start taking one. Cholesterol-lowering meds and anti-seizure meds both negatively interact with biotin.
9. Eosinophilic Pleuropericardial Effusion
Reported only once, Eosinophilic Pleuropericardial Effusion, a very rare condition, was noted in a woman who was taking vitamin B5 and vitamin B7 (biotin). She experienced a severe reaction that happened when the air and blood entered the pleural cavity area around the lungs, and caused a major pulmonary infection. This condition became life-threatening.
10. Acute Respiratory Problems
Acute respiratory issues or even anaphylactic shock can be triggered in people who take large doses of biotin. See your doctor immediately if this happens to you.
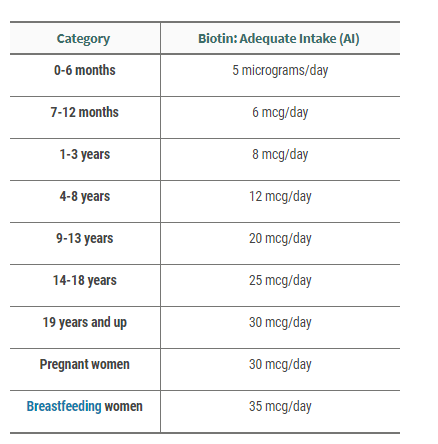
How Much Biotin Should You Take?
Can you take too much biotin? No. An adequate intake of biotin has been set by the Institute of Medicine. Find out what it is and stick to that amount. Whether you get this sufficient amount from the foods you eat, or if you need to take a supplement, this amount should be just right for supporting good health.
Anyone who is experiencing biotin overdose symptoms should follow these guidelines carefully and see a doctor right away. First, stop taking biotin supplements immediately. If the overdose is severe, cut back on biotin-rich foods, but not so much that the body swings to the other extreme.
Drink lots of water to dissolve any toxic substances. Drinking plenty of water will flush the excess water from the body. Take activated charcoal (either tablets or powdered form). Charcoal rids the body of toxins.
If the overdose is extreme, a doctor may treat with a gastric lavage. A tube inserted through the nose down to the stomach. A special fluid is pushed through the tube that washes out all the excess biotin from the body through the urinary tract.
Despite the possible side effects from taking too much biotin, you won’t have a problem if you take biotin as directed. If you’ll keep the following guidelines in mind, you can take biotin with peace of mind.